Problem Statement
- Plan motions for non-holonomic systems whose dynamics are described by an ordinary differential equation of the form $$\dot{q} = f(q,u)$$
- Compute the dynamically feasible and collision free motions for these systems using RRt and KPIECE planners
- Learn about and implement a new planner called Reachability-Guided RRT (RG-RRT)
Results
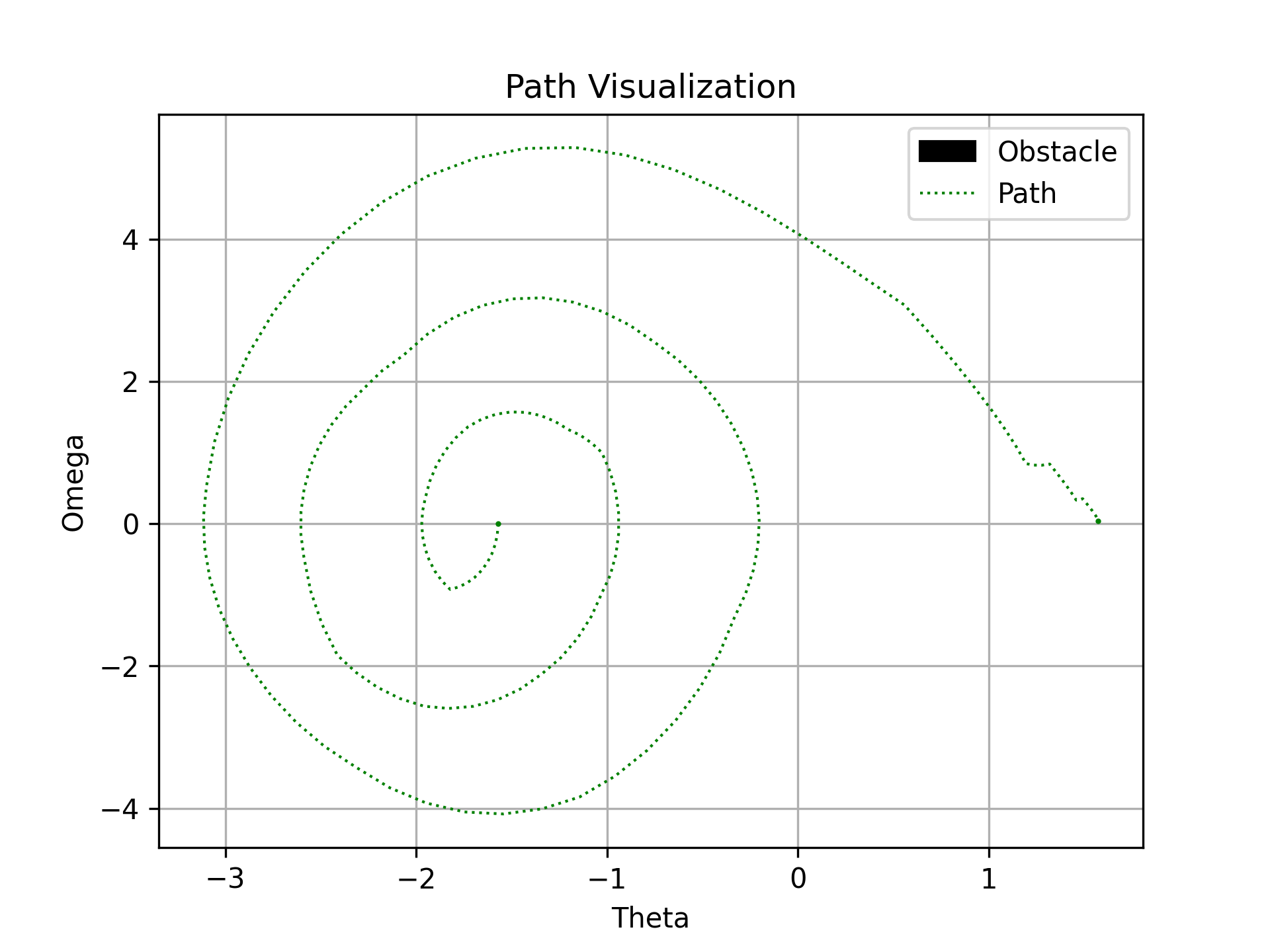
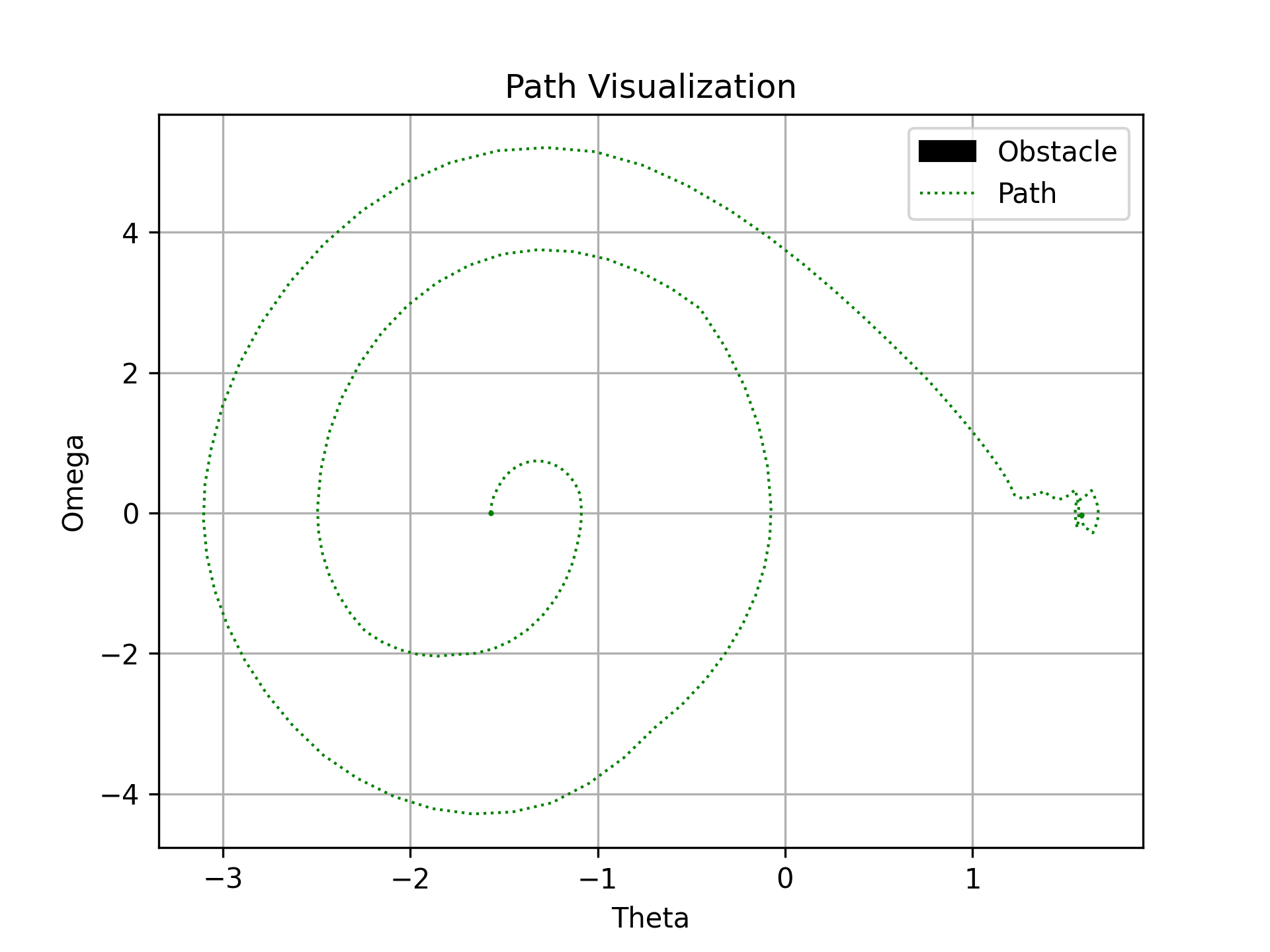
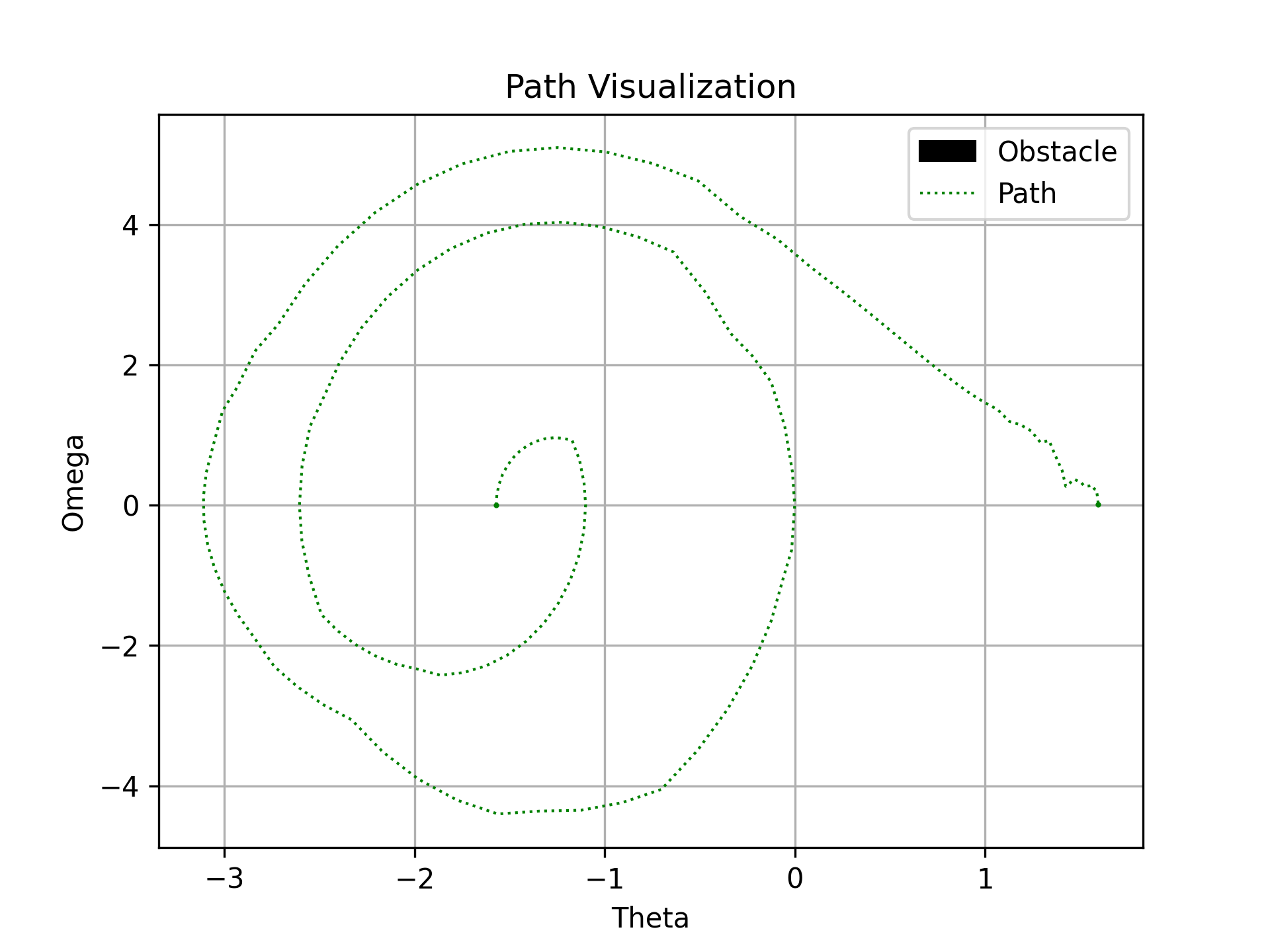
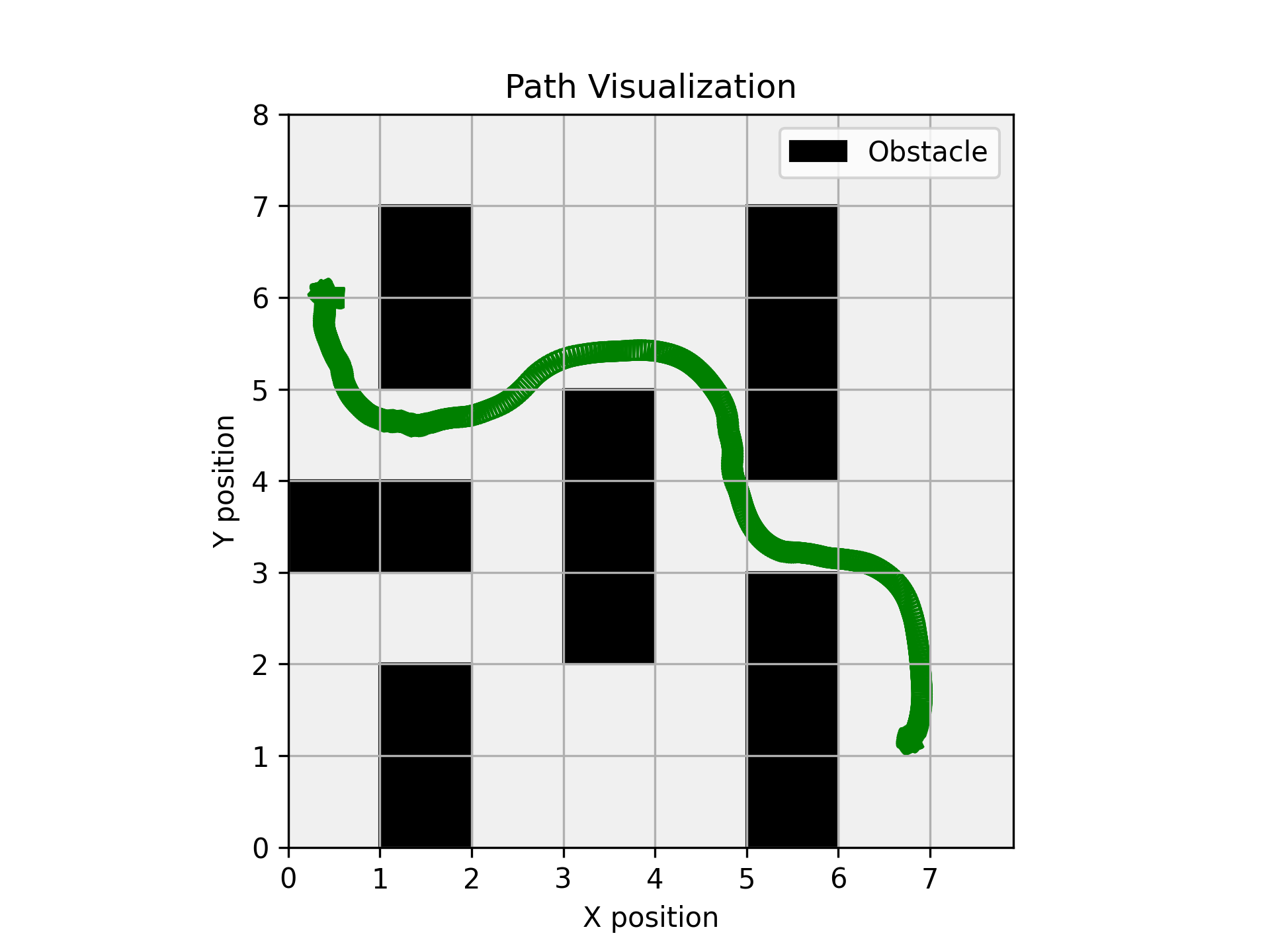
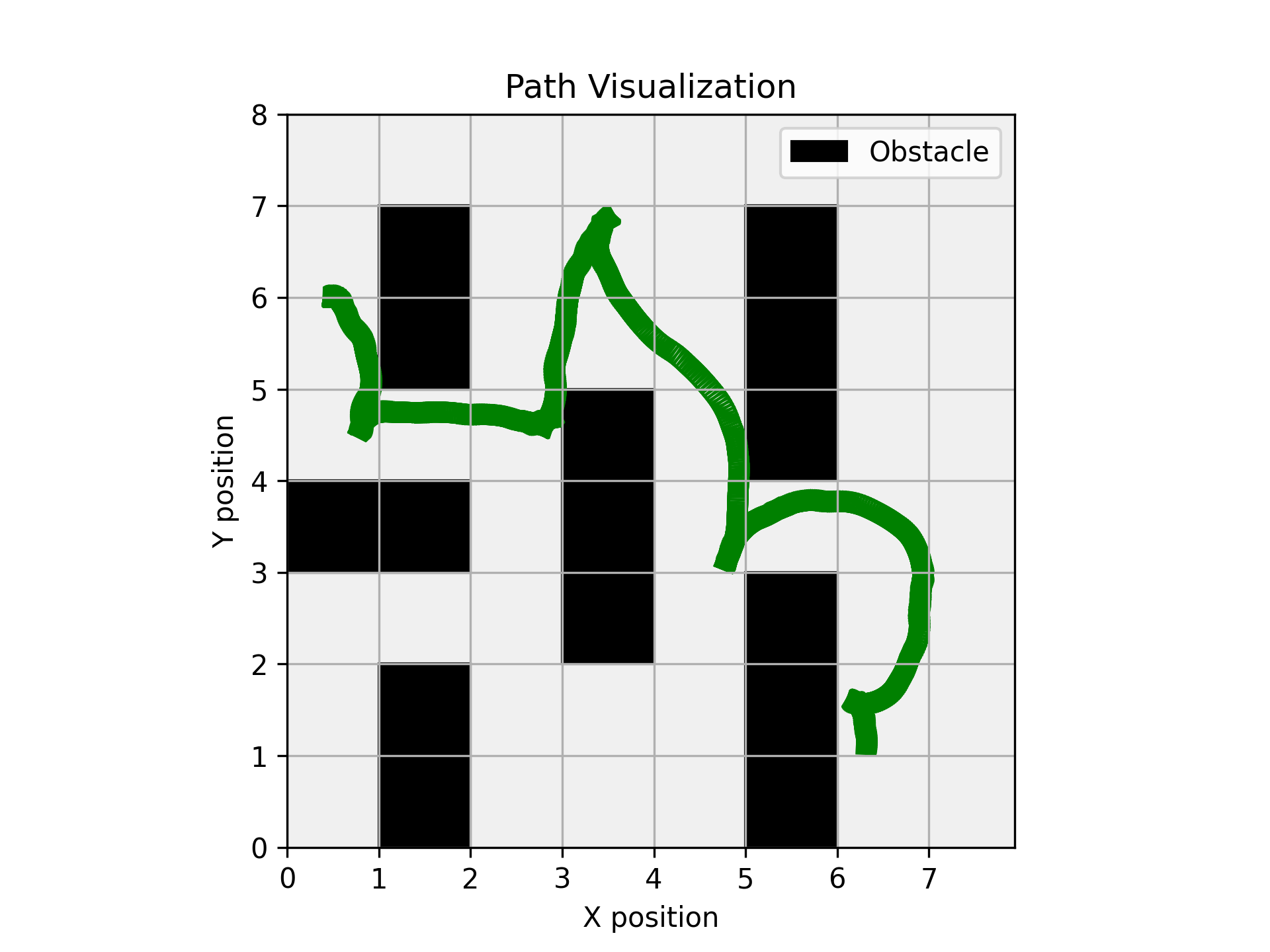
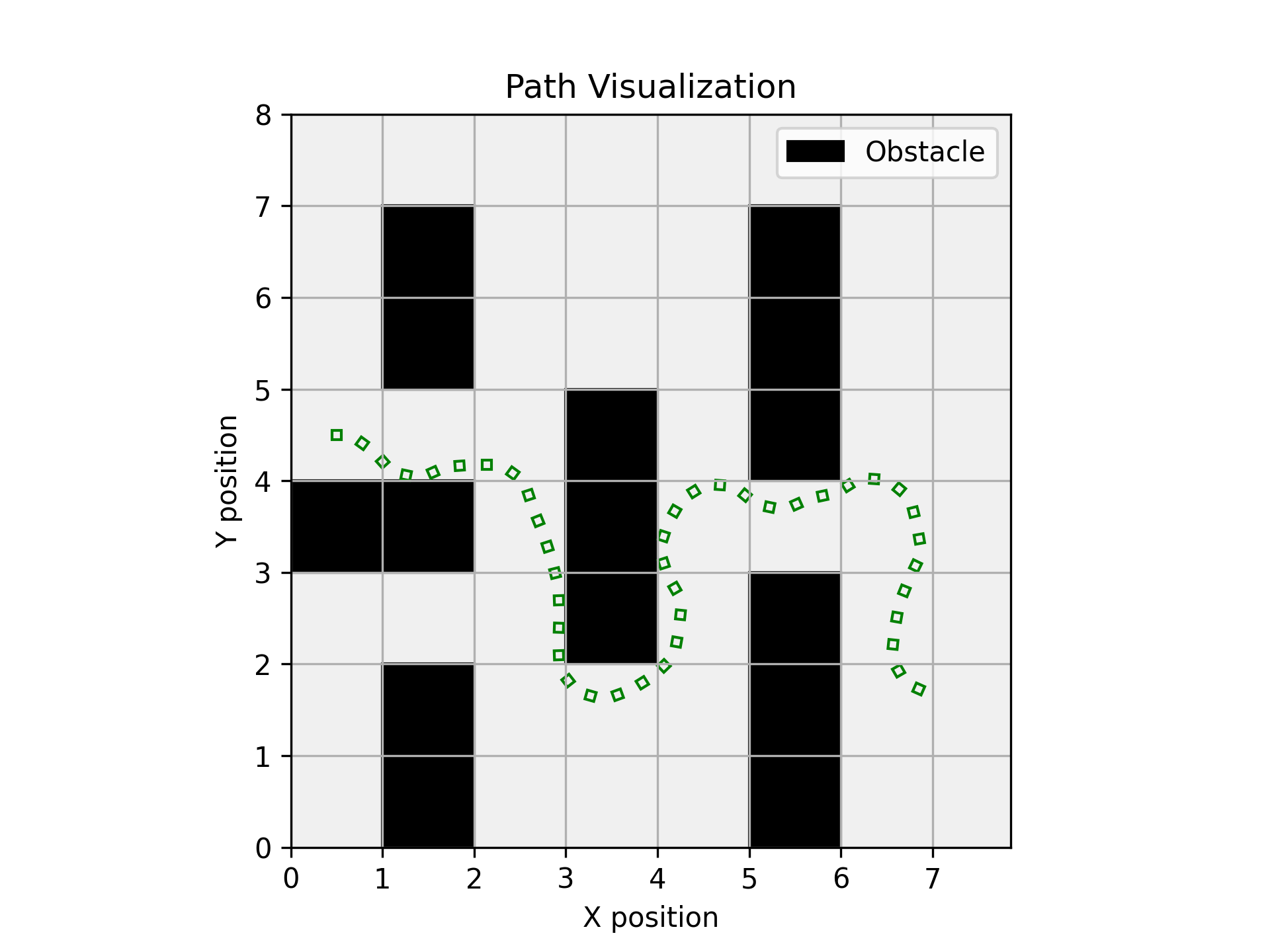
The path for the three different planners KPIECE RRT and RGRRT are shown below:
Pendulum Path planners. Left image shows KPIECE planner, middle image RRT and right image shows RGRRT planner.
Car Path planners. Left image shows KPIECE planner, middle image RRT and right image shows RGRRT planner.
Benchmarking of the planners for both cases were perofrmed and the results obtained as shown below:
Pendulum
| Computation Time |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Computation Time |
| Min | Close to KPIECE | Least | Highest |
| Max | Highest | Close to RRT | Lowest |
| Median | Highest | Least | Close to RRT |
| 1st Quartile | Close to RGRRT | Least | Highest |
| 3rd Quartile | Highest | Least | Higher than RGRRT |
| Inter-Quartile Range | Widest | Smallest | Higher than KPIECE |
| Solution Length |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Solution Length |
| Min | Significantly high | Highest | Least |
| Max | Significantly high | Highest | Least |
| Median | Significantly high | Highest | Least |
| 1st Quartile | Significantly high | Highest | Least |
| 3rd Quartile | Significantly high | Highest | Least |
| Inter-Quartile Range | Similar to KPIECE | Highest | Least |
| Tree Nodes |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Tree Nodes |
| Min | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| Max | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| Median | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| 1st Quartile | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| 3rd Quartile | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| Inter-Quartile Range | Highest | Similar to RGRRT | Least |
| Success Rate |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Success Rate |
| Approximate solution | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Summarizing from the above table, we conclude that:
- The median path length for RGRRT is the least.
- The median number of tree nodes is very low for RGRRT.
Car
| Computation Time |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Computation Time |
| Min | Higher than RGRRT | Highest | Least |
| Max | Close to KPIECE | Least | Highest |
| Median | Close to KPIECE | Highest | Least |
| 1st Quartile | Close to KPIECE | Highest | Least |
| 3rd Quartile | Close to KPIECE | Highest | Least |
| Inter-Quartile Range | Close to KPIECE | Smallest | Widest |
| Solution Length |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Solution Length |
| Min | Highest | Least | Close to KPIECE |
| Max | Highest | Higher than RGRRT | Least |
| Median | Highest | Least | Very close to KPIECE |
| 1st Quartile | Highest | Least | Very close to KPIECE |
| 3rd Quartile | Highest | Close to RGRRT | Least |
| Inter-Quartile Range | Highest | Higher than RGRRT | Least |
| Tree Nodes |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Tree Nodes |
| Min | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| Max | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| Median | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| 1st Quartile | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| 3rd Quartile | Highest | Significantly high | Least |
| Inter-Quartile Range | Highest | Higher than RGRRT | Least |
| Success Rate |
| RRT | KPIECE | RGRRT | Success Rate |
| Approximate solution | 100% | 100% | 100% |
Summarizing from the above table, we conclude that:
- The median path length for RGRRT and KPIECE is least and similar to each other. However path length varies more for KPIECE from one iteration to the other.
- The median number of tree nodes is much much less for RGRRT.